Photo Credit: http://www.sheep101.info/201/parasite.html
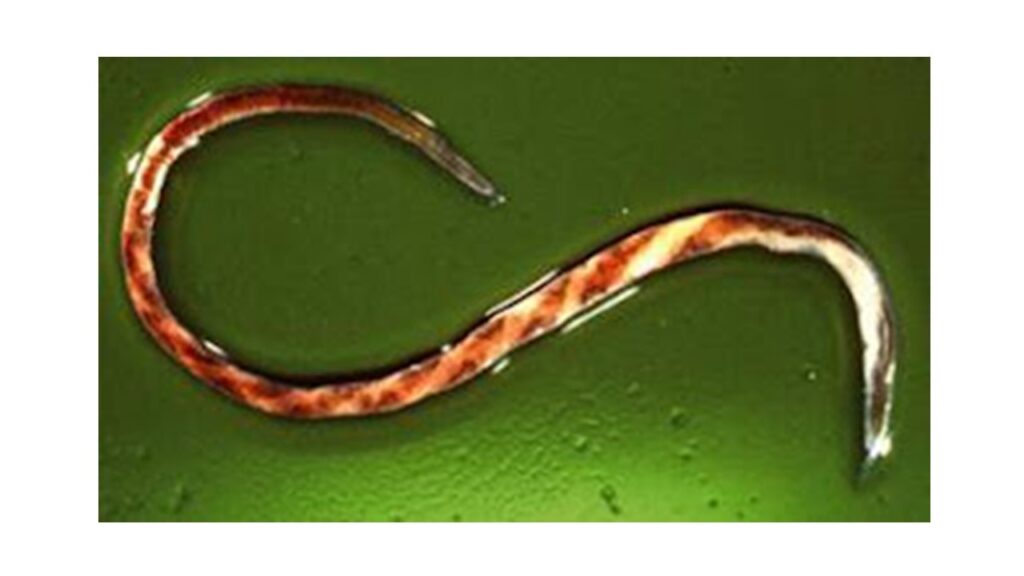
Amid the several parasitic infections that plague ruminants, Haemonchus spp has been recognized as one of the many parasites that cause severe damages to the digestive system. This blood-sucking worm is responsible for a lot of losses in cattle, sheep and goat production.
A parasite generally is any organism, that lives in or on another (host) and harms or offers no advantage to the other organism (host).
This worm also commonly referred to as Barber’s Pole worm resides in the abomasum of ruminants (fourth or last chamber of the ruminant’s stomach). Haemonchus spp has piercing mouthparts that causes extensive damage to the walls of the abomasum. An adult worm is capable of sucking about 0.05mls of blood daily from an affected animal. Hence an animal infected with about 2000 worms will have 100mls of blood loss daily.
There are various species of the blood parasite affecting various ruminant types. Some of the common species of Haemonchus include Haemonchus contortus, Haemonchus similis and Haemonchus placei. There are few records of cross-transmission of the Haemonchus spp between small ruminants and cattle. Haemonchosis has remained a threat to ruminant production especially in the tropical, subtropical and warm temperate regions of the world, where environmental conditions favour the free-living stages of the parasite.
CLINICAL SIGNS & DIAGNOSIS
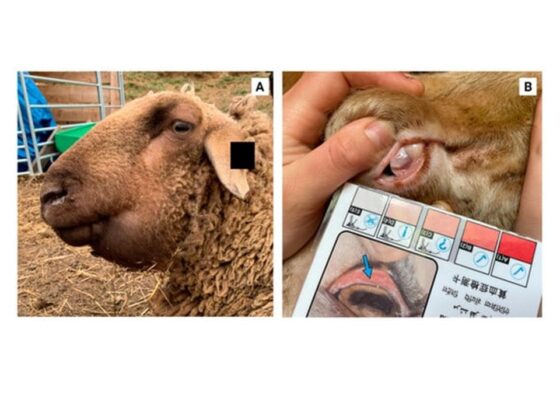
In acute conditions, anaemia, agalactia in ewes, submandibular oedema or bottle jaw and death due to blood loss are among the common clinical signs. When the condition becomes chronic, there is progressive weight loss and general weakness. Diagnosis is based on presenting clinical signs, grazing history as well as worm egg count from the laboratory.
TREATMENT & PREVENTION
Consult your veterinarian once you notice similar signs on your farm. Having a good management program to control parasitic infection on your farm is important.